
10 Key Elements of a Product Strategy Framework
Building a successful product takes more than instinct or a strong vision. Product teams need a structure that connects market realities, user behavior and business goals so they can make clear decisions and ship products that matter. A product strategy framework gives teams that structure by aligning your strategy and providing consistent support for decision-making to keep the entire product team focused on outcomes instead of output.
Done well, a product strategy framework acts as your north star. It defines the direction, the reasoning behind key decisions and the steps teams take to deliver value fast.
Key Takeaways
A product strategy framework connects your product vision, market research, user needs and business goals
It gives product managers a repeatable way to prioritize features, reduce risk and adapt to market shifts
Core components include a product vision, target market, product goals, competitive analysis, product roadmap, pricing strategy and KPIs
Proven frameworks like OKRs, RICE and Lean Startup help teams turn strategy into action
Digital experience analytics strengthen product decisions with real user behavior data
What Is A Product Strategy Framework?
A product strategy framework is a structured model that helps product teams turn a product vision into an actionable strategy. It outlines the inputs, decisions and processes needed to guide product development from idea through launch and beyond.
A strong framework keeps teams aligned on what you’re building, why it matters and how you plan to deliver it. It also helps product managers evaluate trade-offs, understand user needs and adapt decisions as market conditions evolve.
Product Vision vs. Product Strategy vs. Strategy Framework
These terms often overlap, but each plays a different role:
Product vision is your long-term direction. It explains the impact you want the product to create and the problem it solves.
Product strategy is the plan for delivering that vision. It outlines how you’ll reach your goals, who you’ll serve and the value you’ll deliver.
Product strategy framework is the structure you use to build and maintain the strategy. It keeps the vision and strategy aligned with research, data and business goals.
Why A Product Strategy Framework Matters
A product strategy framework is more than documentation. It gives product managers and product teams a predictable way to align decisions with user needs, market research and business goals. With a framework in place, teams can evaluate new ideas, adapt to market shifts and focus on the work that drives product success.
A strong product strategy framework helps answer questions like:
Does a new idea support the target market and user needs?
Does it align with product goals and business goals?
Can it fit into the product roadmap without disrupting priorities?
Is it feasible based on resources, pricing strategy or delivery channels?
This structure keeps teams grounded in evidence instead of assumptions, which reduces risk and improves long-term outcomes.
7 Benefits of Creating a Product Strategy
Team alignment: A clear product strategy framework ensures everyone—from engineering to marketing—shares the same understanding of the target market, value proposition and product differentiators.
Clear prioritization: The framework guides roadmap decisions so teams focus on the initiatives that support product goals, user needs and business objectives.
Improved decision making: Product managers can evaluate ideas based on data, user behavior and strategic impact. This reduces noise, prevents distractions and helps teams prioritize with confidence.
Enhanced customer focus: By defining user needs and target audience profiles, the framework helps teams build features that solve real pain points instead of perceived ones.
Greater competitive advantage: Structured market research and competitive analysis highlight opportunities to differentiate the product and strengthen your positioning.
Improved ability to manage risk: With a consistent method for analyzing user needs, market trends and resource constraints, product teams can adjust course without increasing the risk of failure.
Increased likelihood of product market success: A strong framework reduces the risk of misalignment, improves product market fit and helps create products that users adopt and stay loyal to.
10 Core Components of an Effective Product Strategy Framework
The strongest product strategy frameworks give product managers a complete picture of the target market, user needs, product goals and business objectives. These components work together to guide decisions, reduce risk and support product success across the entire product development process.
Below are the essential elements every product strategy framework should include.
1. Product Vision
Your product vision defines the purpose of your product and the outcome you want to create. It should answer:
Who the product is for
What problem it solves
Why it matters
What success looks like
A clear vision directs the strategy without dictating the solution, which gives teams space to innovate.
2. Target Market
Your product strategy framework needs a clear definition of the target market. This helps shape market research, refine product positioning and guide decisions about pricing, messaging and distribution.
3. User Needs
Great products solve real problems. Understanding user needs—pain points, behaviors, motivations and decision-making patterns—ensures your product strategy focuses on what matters most.
Use tools like usability testing, product analytics, session replays and voice of customer (VoC) programs to gather firsthand insight.
4. Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Market research helps you understand market conditions, market trends and broader industry shifts. Competitive analysis highlights:
What alternatives offer
How users perceive competing products
Where the gaps and opportunities are
These insights inform your differentiation strategy and guide your pricing strategy, roadmap and product positioning.
5. Business Objectives
Your product strategy framework must connect to measurable business goals. Examples include:
Grow market share of 10% in two years
Acquire 1,000 active users within six months of launch
Achieve monthly recurring revenue of $10k from the product
These objectives stay tied to meaningful outcomes.
6. Product Goals
Product goals translate business objectives into product-specific targets. They define what winning looks like, guide prioritization and help product managers evaluate new initiatives. Examples include:
Increase activation rate
Improve retention
Reduce support volume
Drive expansion revenue
Strong goals prevent teams from spending time on low-impact ideas.
7. Pricing Strategy
Pricing is both a business decision and a product strategy decision. Your pricing strategy should reflect customer willingness to pay, competitive benchmarks, value delivered and long-term profitability goals.
Pricing also signals positioning. Premium pricing, cost leadership and freemium models all shape how customers perceive your product.
8. Distribution Channels
Distribution determines how customers discover, access and use your product. Channels may include web, mobile, partner ecosystems, app marketplaces or content-driven acquisition.
Your distribution strategy also influences product design, integrations and onboarding.
9. Product Roadmap
The product roadmap translates the strategy into sequenced work. It outlines priorities, timelines and upcoming product initiatives.
A great roadmap:
Reflects product goals and user needs
Evolves as you gather new data
Helps stakeholders understand what’s coming and why
Product managers often use frameworks like RICE to prioritize objectively.
10. Performance Metrics and KPIs
Your product strategy framework needs clear KPIs so teams can measure progress and validate decisions.
Common KPIs include:
Activation rate
Adoption
Conversion
Retention
Customer satisfaction
Revenue or MRR
Performance metrics ensure the strategy stays grounded in real results and continuous learning. Check our blog on essential product metrics to find out which ones will be most relevant to your goals
5 Common Types Of Product Strategies
Different product strategies fit different markets and product goals. These strategy types give product leaders a starting point for defining how the product will compete.
Differentiation strategy: You create unique product value that competitors can’t easily match. This could be speed, design, user experience, intelligence or specialized capabilities.
Cost strategy: You compete on price by offering more value at lower cost or delivering essential features affordably.
Quality strategy: You offer higher-quality features, customer support or user experience. SaaS companies often use quality as a differentiator through performance, availability and service.
Focus or niche strategy: You target a specific, well-defined audience with tailored capabilities. This strategy works well when broad-market competitors overlook niche needs.
Growth strategy: You expand the product into new markets or add capabilities that increase reach and impact. Growth strategies often rely on market trends and strong competitive analysis.
10 Proven Product Strategy Frameworks And Models
Leveraging a proven framework can streamline the execution of the product strategy. There are a plethora of popular frameworks available for companies to use:
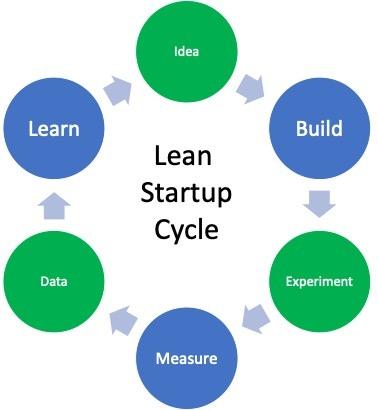
1. Lean startup methodology: The lean methodology is considered an efficient and hyper-practical strategy for developing processes. It centers on building a minimum viable product (MVP), testing it with customers, gaining feedback and improving the product in iterations.
2. Kano method: The Kano method is named after business consultant Noriaki Kano. It helps businesses build user-centered products by categorizing customer requirements into five categories: basic needs, performance needs, excitement needs, indifferent needs and reverse needs. Businesses can use this system to understand customer desires and prioritize feature development accordingly.
3. OKR method: The OKR method was created by Google and stands for objective and key results. It involves setting objectives for the project and then tracking how development progresses through smaller milestones toward those objectives. By following the OKR framework, teams can stay aligned on project goals while objectively evaluating their results and processes.
4. Ansoff model: The Ansoff model, often referred to as the product and market expansion grid, is used to help companies identify growth and expansion opportunities while analyzing associated risks. It offers four strategies that support this: market penetration, product development, market development and diversification.
5. The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) matrix: Also known as the growth/share matrix, the BCG matrix is designed to help with long-term strategic planning and decide where to invest for the future. Companies use it to evaluate the growth potential and strategic importance of different products and features within a product line.
6. The SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis is extremely valuable for product managers who are looking to evaluate and improve their products and features. This framework looks at the strengths, opportunities, weaknesses and threats. A SWOT analysis gives product managers a comprehensive understanding and helps identify areas for improvement. By regularly conducting a SWOT analysis, product managers can remain competitive and stay ahead of the competition.

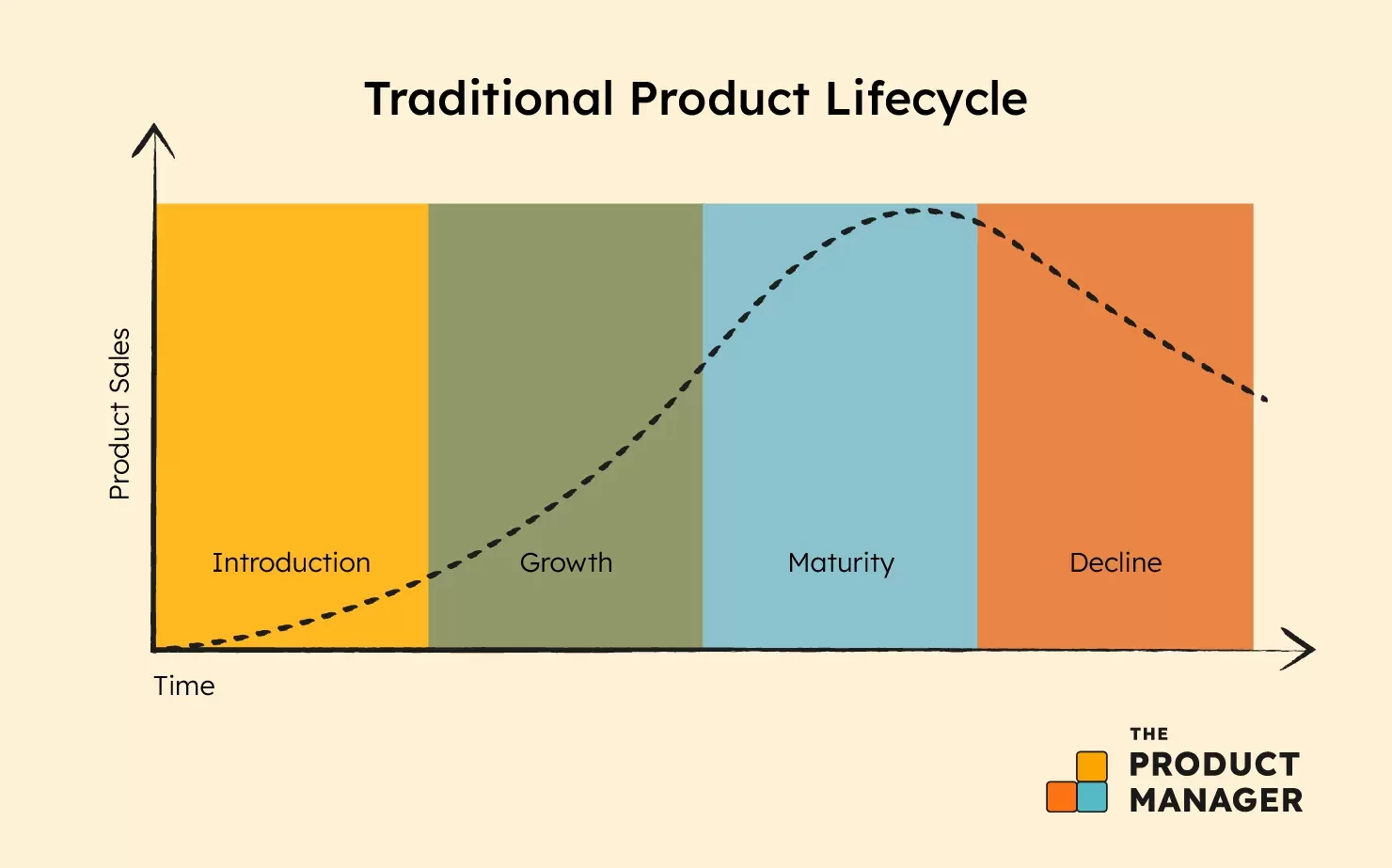
7. Product lifecycle: The product lifecycle framework helps companies understand the different stages that a product goes through. The lifecycle consists of the following stages: development, introduction, growth, maturity and decline.
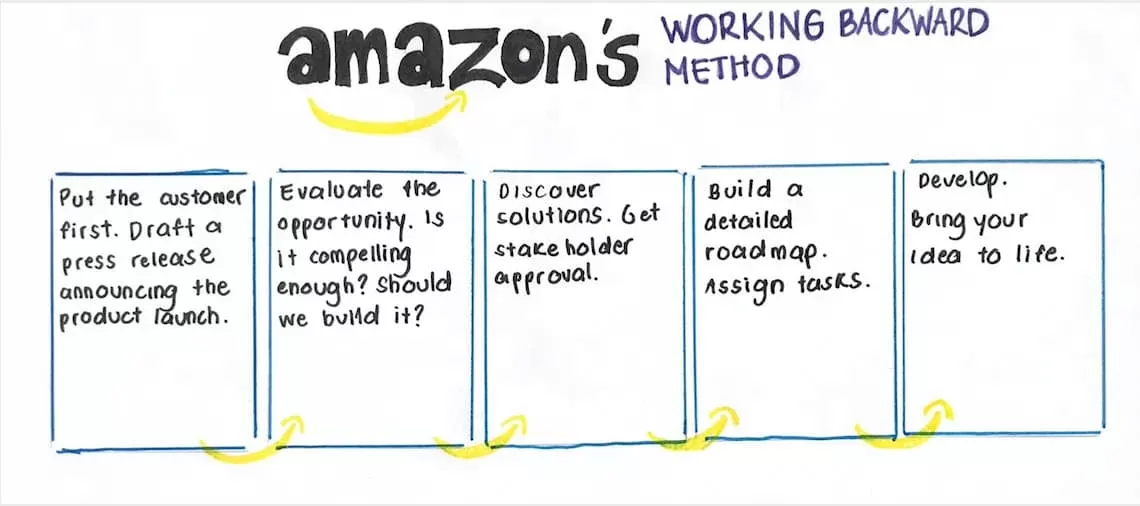
8. Working backward (the Amazon method): Amazon is credited with developing the working backward method, where product managers are encouraged to start at the final step of releasing a product. The product team’s first step is to write an internal only press release announcing the product. This helps teams determine if the product is worth building. Using this method also helps product teams package the product idea up to present it to leadership, the DevOps team and eventually customers.
9. Focus strategy: A focus strategy is an approach to building a product or features to appeal to a niche market. This enables product teams to focus on a specific audience instead of a broader one that tries to appeal to everyone. For example, a bank may choose to provide specialized features on its app to a specific age range for education loans.
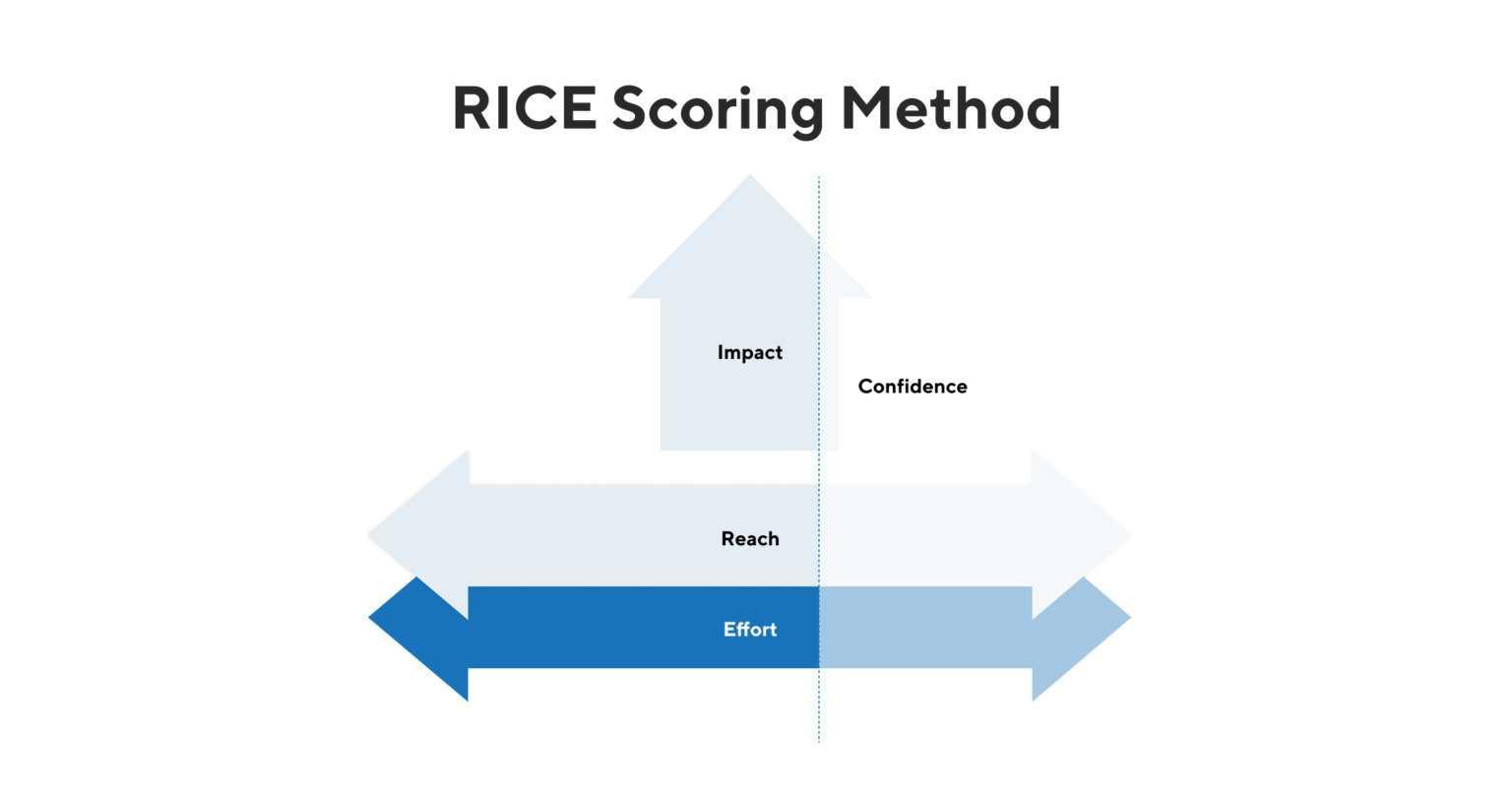
10. RICE scoring model: This model helps product managers determine which products and features to put on their roadmaps by scoring the items according to four factors: reach, impact, confidence and effort.
How To Turn Your Product Strategy Framework Into an Actionable Development Plan
A product strategy is only useful if teams can execute on it. These steps connect your strategy to day-to-day decisions across the product team.
Step 1: Set Product Goals and Define Tasks
Break your product goals into clear tasks across design, engineering, research and product management. Keep goals focused and measurable.
Step 2: Prioritize the Roadmap
Use data, user needs and scoring models to sequence work. Avoid prioritizing based on pressure or assumptions.
Step 3: Allocate Resources Across the Product Team
Assign owners, define cross-functional collaboration and determine any constraints around time or budget.
Step 4: Track KPIs and Measure Progress
Monitor leading and lagging indicators. Share essential KPIs across stakeholders so teams stay aligned.
Step 5: Review and Iterate Based on Market Conditions and User Behavior
Strategy isn’t static. Use real user behavior, market trends and product performance data to refine your product roadmap.
Checklist: What Every Product Strategy Framework Needs
Use this checklist to ensure your product strategy framework is complete, actionable and grounded in real user and market insight.
- Understand the market: Gather market research to identify your target customers, their needs and the competitive landscape.
- Define your product vision: Clarify the problem you solve, who the product is for and the outcome you want to create. This anchors every decision.
- Identify your target market and user needs: Use data from usability testing, analytics and CoC programs to understand behaviors, pain points and preferences.
- Set business and product goals: Establish measurable business objectives and translate them into product goals that guide prioritization and planning.
- Shape your product positioning: Articulate your value proposition and how the product stands apart from alternatives.
- Build a prioritized product roadmap: Sequence work based on user needs, business goals and scoring models like RICE.
- Define your pricing and distribution strategy: Determine how customers will discover, access and pay for your product.
- Choose KPIs and create a measurement plan: Track the metrics that reflect product performance and product market fit.
- Align your team: Make sure every team member understands the product strategy framework and their role in executing it.
- Create a process for iteration: Use data and user behavior insights to refine the strategy as markets shift and new information emerges.
FAQs
What is a product strategy?
A product strategy guides how a product team delivers the product vision. It defines the target market, user needs, product goals and the plan for reaching them.
Why is a product strategy framework important?
It helps teams align decisions, prioritize effectively, reduce risk and stay focused on user needs and business goals.
What are examples of product strategies?
Common strategies include differentiation, cost leadership, quality, focus and growth strategies.
How does a product manager create a product strategy framework?
They analyze the market, define the product vision, set product goals, perform competitive analysis, build the roadmap and establish KPIs. They also use data and user behavior insights to adapt the strategy over time.
Strengthen Your Product Strategy With Glassbox
A successful product strategy depends on understanding what users do, where they struggle and why they convert. Glassbox gives product managers real-time visibility into user behavior across digital journeys so you can make confident decisions backed by evidence.
From uncovering friction to validating new product initiatives, Glassbox helps teams build products that stand out. Explore how digital experience intelligence supports a stronger product strategy framework with Glassbox’s Product Management & UX Solutions.




